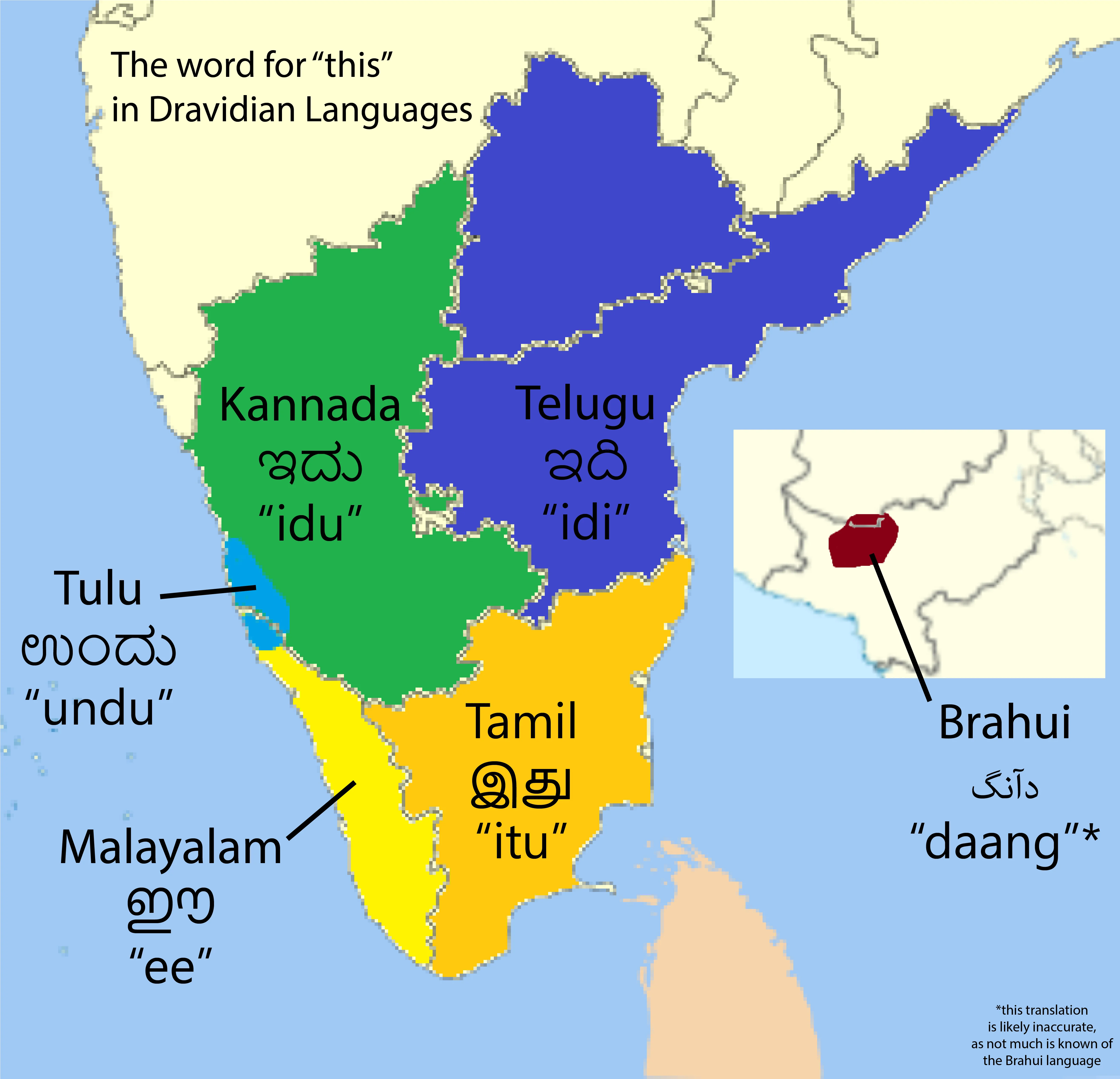
South Indian Languages (Dravidian Languages)
- The major languages spoken in South India belong to the Dravidian language family, which is entirely different from the Indo-Aryan family that includes Hindi. The four most widely spoken South Indian languages are Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, and Malayalam. These languages share some linguistic similarities but are distinct in terms of script, phonology, and grammar.
Common Features of South Indian Languages:
- Dravidian Roots: Unlike Hindi and other Indo-Aryan languages, South Indian languages derive from the Dravidian family, which has a distinct structure and grammar.
- Scripts: Each language uses its own unique script, though all scripts are derived from ancient Indian scripts like Brahmi.
- Literary Traditions: South Indian languages boast rich classical literature, with Tamil being one of the oldest continuously spoken languages in the world.